COORDINATOON OF PHYSIOLOGICAL FUNCTIONS
● The functions of the `color{violet}("organs/organ systems")` in our body must be coordinated to maintain `color{brown}("homeostasis.")`
● `color{brown}("Coordination")` is the process through which two or more `color{violet}("organs interact")` and complement the functions of one another.
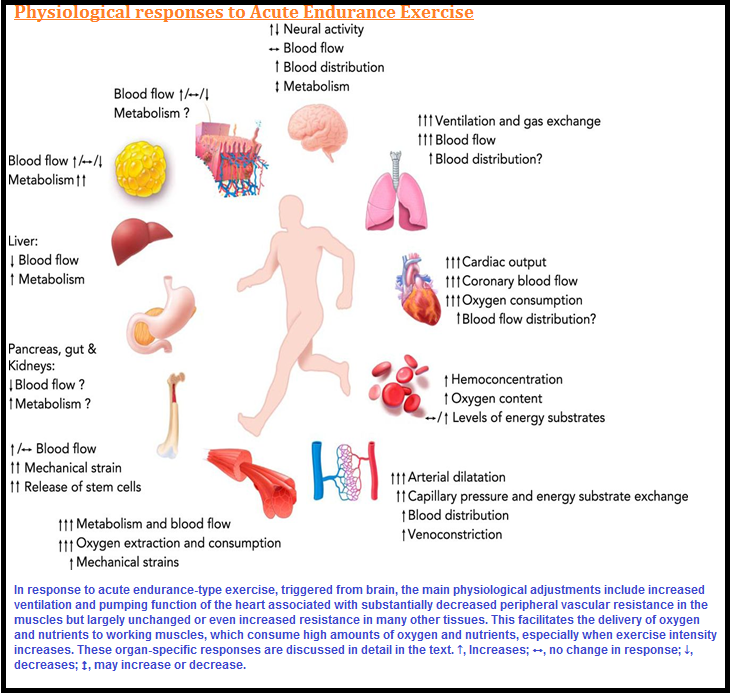
● For example, when we do physical exercises, the `color{violet}("energy demand")` is increased for maintaining an increased muscular activity.
● The `color{violet}("supply of oxygen")` is also increased.
● The increased `color{violet}("supply of oxygen")` necessitates an increase in the rate of respiration, `color{violet}("heart beat")` and increased `color{violet}("blood flow via blood vessels.")`
● When physical exercise is stopped, the activities of `color{violet}("nerves, lungs, heart")` and `color{violet}("kidney")` gradually return to their normal conditions.
● Thus, the functions of `color{brown}("muscles, lungs, heart, blood vessels, kidney")` and `color{brwn}("other organs")` are coordinated while performing physical exercises.
● In our body the `color{brown}("neural system")` and the `color{brown}("endocrine system")` jointly coordinate and integrate all the activities of the `color{violet}("organs")` so that they function in a `color{violet}("synchronised fashion.")`
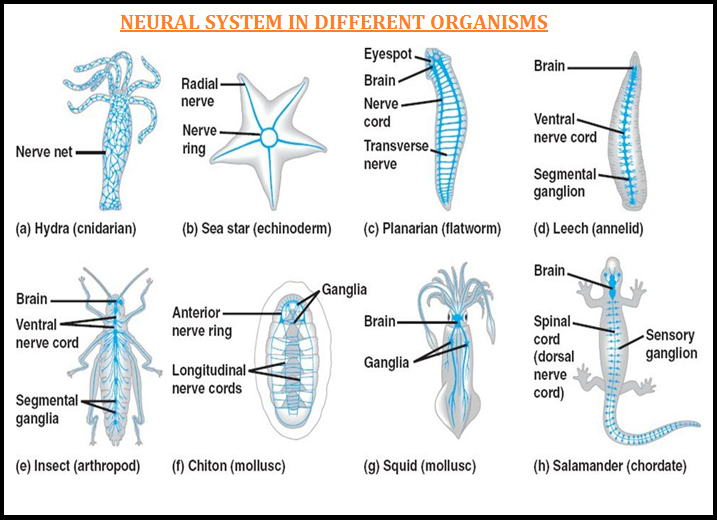
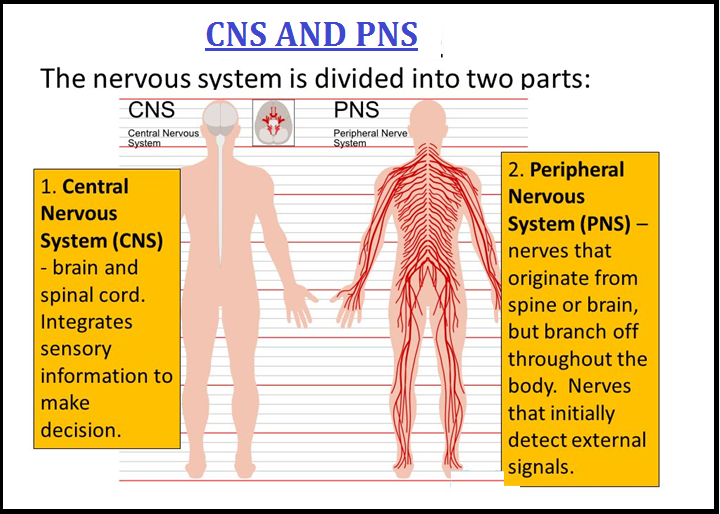
● The `color{violet}("neural system")` provides an organised network of `color{brown}("point-to-point connections")` for a `color{violet}("quick coordination.")`
● The `color{violet}("endocrine system")` provides `color{brown}("chemical integration")` through `color{violet}("hormones. ")`
● `color{brown}("Coordination")` is the process through which two or more `color{violet}("organs interact")` and complement the functions of one another.
● For example, when we do physical exercises, the `color{violet}("energy demand")` is increased for maintaining an increased muscular activity.
● The `color{violet}("supply of oxygen")` is also increased.
● The increased `color{violet}("supply of oxygen")` necessitates an increase in the rate of respiration, `color{violet}("heart beat")` and increased `color{violet}("blood flow via blood vessels.")`
● When physical exercise is stopped, the activities of `color{violet}("nerves, lungs, heart")` and `color{violet}("kidney")` gradually return to their normal conditions.
● Thus, the functions of `color{brown}("muscles, lungs, heart, blood vessels, kidney")` and `color{brwn}("other organs")` are coordinated while performing physical exercises.
● In our body the `color{brown}("neural system")` and the `color{brown}("endocrine system")` jointly coordinate and integrate all the activities of the `color{violet}("organs")` so that they function in a `color{violet}("synchronised fashion.")`
● The `color{violet}("neural system")` provides an organised network of `color{brown}("point-to-point connections")` for a `color{violet}("quick coordination.")`
● The `color{violet}("endocrine system")` provides `color{brown}("chemical integration")` through `color{violet}("hormones. ")`